Velocity vs. Acceleration
Velocity and acceleration describe the motion of an object and are related. Both are measurable quantities with magnitude and direction. However, there are similarities and differences between the two.
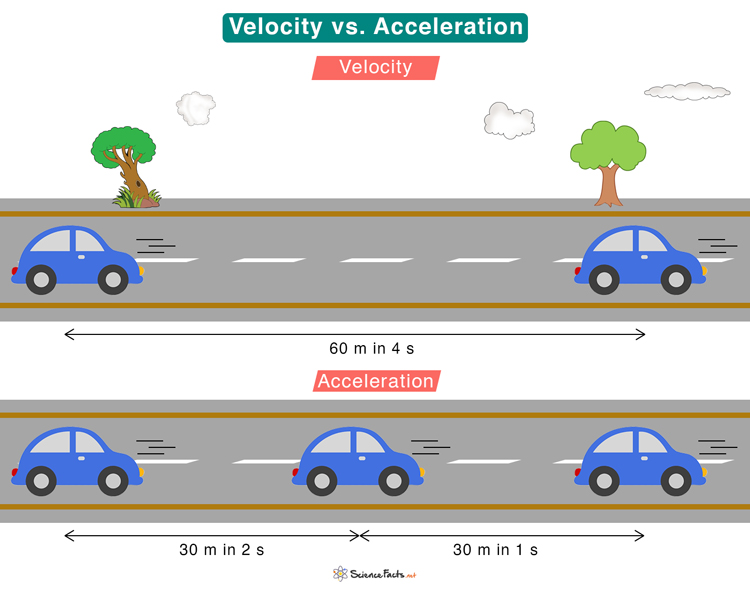
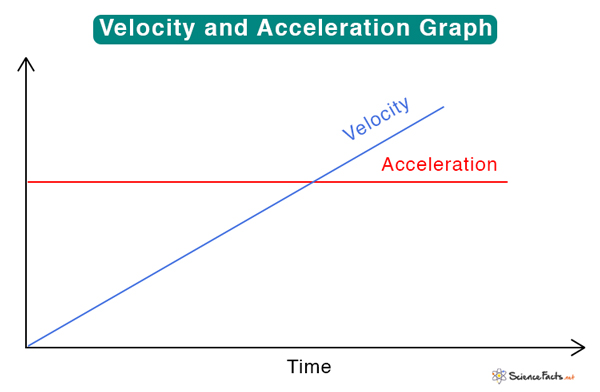
Velocity is a measure of the rate of change of displacement. When an object moves from one position to another, it is said to be displaced. The value of displacement over time gives the velocity. Its direction is along the displacement.
On the other hand, acceleration measures the rate of change in velocity. The object may change its speed or direction while keeping the speed constant. In both cases, it experiences acceleration. While acceleration refers to an increase in speed over time, its opposite, when the speed decreases with time, is called deceleration.
Difference Between Velocity and Acceleration
The table below shows the significant differences between the two.
| Property | Velocity | Acceleration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rate of change of displacement | Rate of change of velocity |
| Nature | Vector. It has both magnitude and direction. | Vector. It has both magnitude and direction. |
| Symbol | v | a |
| Formula | Velocity = Change in displacement/Time interval v = Δx/Δt | Acceleration = Change in velocity/Time interval a = Δv/Δt |
| SI unit | Meters per second or m/s | Meters per second squared or m/s2 |
| Imperial unit | Feet per second or ft./s | Feet per second squared or ft./s2 |
| Value | It can be positive and negative. Zero velocity implies that the object is stationary. | It can be positive and negative. Zero acceleration implies that the object is moving with a constant velocity. |
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Tuesday, April 18, 2023