Spring Force
What is Spring Force
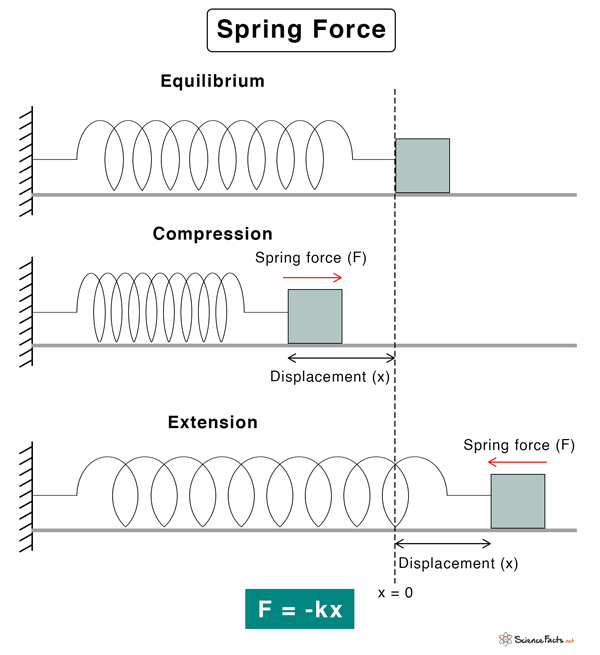
When a metal spring is stretched or compressed, it is displaced from its equilibrium position. As a result, it experiences a restoring force that tends to retract the spring back to its original position. This force is called the spring force. It is a contact force that can be found in elastic materials.
Examples of Spring Force
Here are a few examples of the spring force from everyday life.
- Pendulum
- Rubber band
- Bungee cord
- Keys in a PC keyboard
- Trampoline
- Brakes, clutches, and shock absorbers
- Watches and toys
- Pogo stick
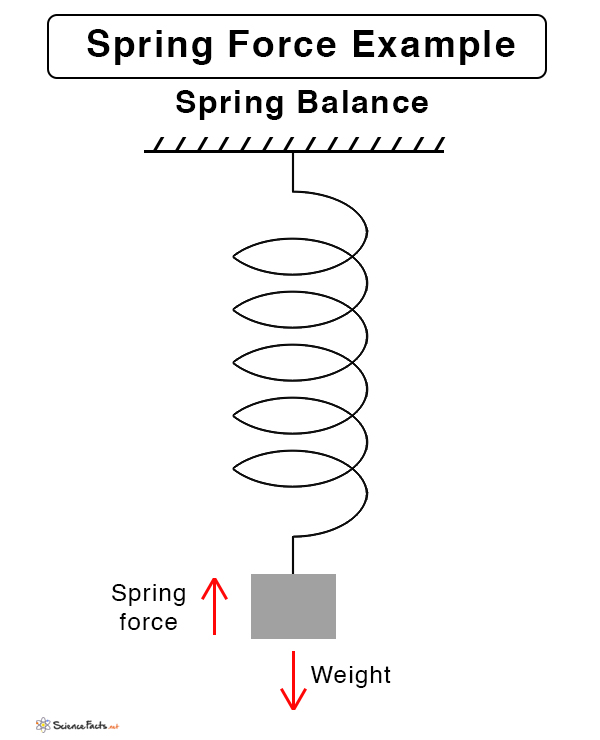
- Spring balance
Spring Force Equation: How to Find the Spring Force
The spring force can be quantified using Hooke’s law. According to this law, when a spring stresses or compresses, the restoring force F is proportional to the displacement x.
F ∝ x
Spring Force Formula:
F = -kx
Unit of Spring Force: Newton or N
Here, k is known as the force constant. The negative sign is because the force is opposite to the displacement, that is, the force displaces the spring from its equilibrium position. This equation applies to both compression and extension of spring. The force can be measured using a spring tester.
The magnitude of the spring constant is given by,
k = F/x
Suppose F = 1 N and x = 1 m, then
k = 1 N/ 1 m = 1 N/m
Therefore, the spring constant is defined as the force required to displace the spring by one meter. It has a unit of Newton per meter (N/m) and a dimension given by MT-2.
Work Done by Spring Force
The work done W by the spring force is given by,
W = F.x
Spring Force on an Object Suspended by a Spring
If an object of mass m is suspended by a spring, then it is displaced by its own weight. The spring force is its weight mg
mg = -kx
Or, |k| = mg/x
The above equation can be used to find the force constant of the spring.
Torsion on a Spring
The above equation for spring constant is applied when the force is along the axis of the spring. In the case of torsion, where the applied force makes a twist in the spring, the equation for k is,
k = P.M/Deg
where,
P = Force exerted on spring
M = Moment arm of the spring
Deg = Angle by which the spring rotates
How to Calculate Spring Force
Example Problem: A spring with a force constant 1300 N/m is loaded vertically with a mass that extends the spring to 6 cm. Find the magnitude of the spring force.
Given,
k = force constant of the spring = 8 kg
x = displacement of the spring = 6 cm = 0.06 m
The magnitude of the spring force is,
F = kx = 1300 N/m x 0.06 m = 78 N
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, December 11, 2020





Great post! I learned a lot about the spring force and its formula. The examples you provided really helped me to understand the concept better. Thanks for sharing your knowledge!
How much average power a healthy man can deliver in his daily life per day . I wish to invent hand made tools without using power for wich used in daily life with man power only by applying simple mechanics.
A healthy person can sustain a power output of around 75 to 150 watts during moderate activities, with higher bursts possible for short periods. To design handmade tools, you can use simple machines like levers, pulleys, and gears to maximize efficiency and reduce effort. Historical examples, such as manual mills and pedal-powered devices, demonstrate how mechanical advantage can be used effectively without external power sources.