Simple Diffusion
What is Simple Diffusion
Simple diffusion is defined as the movement of substances like ions, atoms, and molecules from an area of their higher concentration to lower concentration without the involvement of any other molecules like a carrier protein.
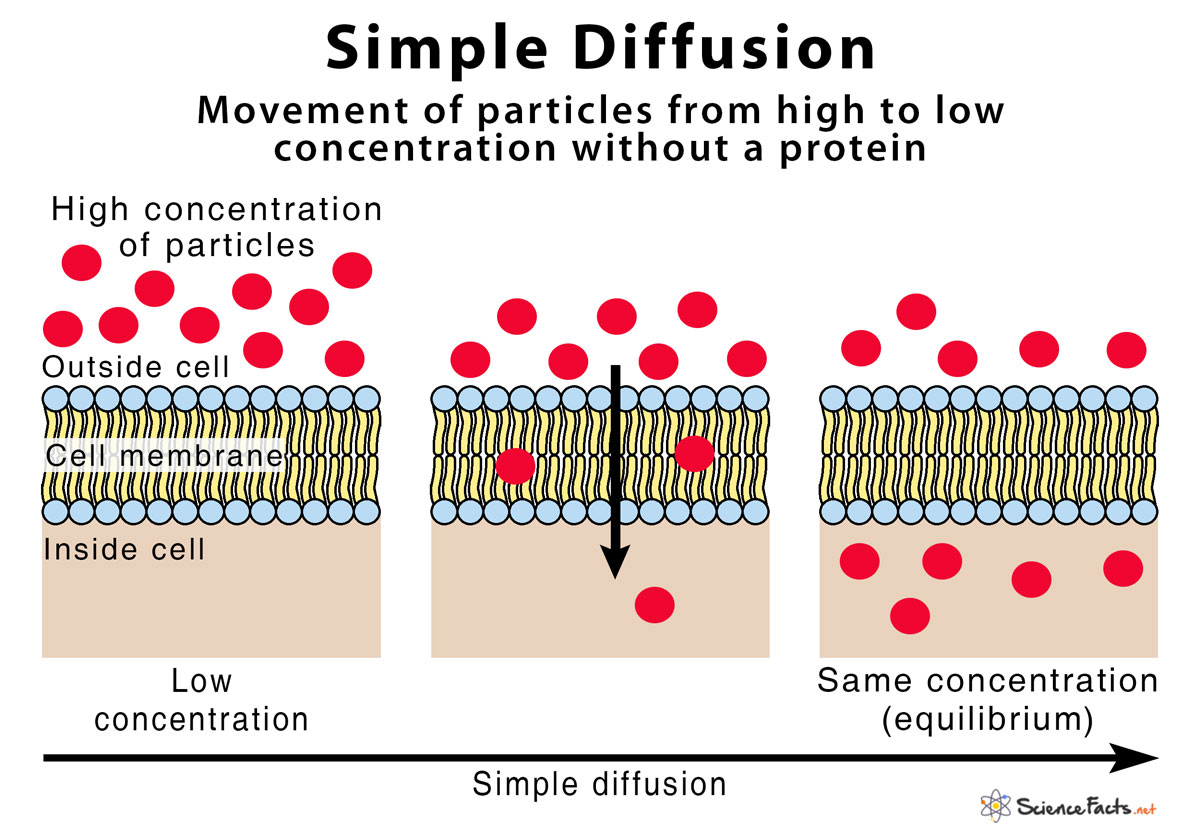
How does Simple Diffusion Work and What happens during the Process
It is a natural phenomenon where the particles move along a concentration gradient in a solution through a semipermeable membrane to attain equilibrium on both sides. Simple diffuson occurs because the particles undergoing this process are always in a state of random motion.
What are the Characteristics of Simple Diffusion
- Occurs across a semipermeable membrane
- Requires a concentration gradient across the cell membrane
- It is a passive transport mechanism thus require no energy expenditure by the cell
- Does not need a carrier transport protein
- Happens by random motion
- Cannot be inhibited by an inhibitor molecule because of the absence of carrier proteins
- Non-specific to any particle
- A comparably slow process than other forms of diffusion
Practical Examples of Simple Diffusion
- Gas exchange in plants with the help of stomata
- Cellular respiration in animals where they breathe in oxygen inside the body and send carbon dioxide out
- The process by which animals including humans get rid of their waste products in the form of urea
- The process by which small, uncharged, and lipid-soluble molecules pass between the phospholipid bilayer of the semipermeable membrane of the cells
- Absorption of nutrients such as carbohydrates, minerals, and vitamins in the small intestine
- Delivering oxygen, water and small nutrients inside the cell of simple organisms like amoeba and bacteria
FAQs
Q1. How is simple diffusion different from active transport?
Ans. Simple diffusion moves substances down its concentration gradient without the involvement of any other molecule and energy expenditure whereas active transport helps in the transport of molecules against the concentration gradient assisted by other protein molecules and requiring energy expenditure by the cell.
Q2. How is simple diffusion different from osmosis?
Ans. Simple diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of their higher to lower concentration whereas osmosis involves the movement of water molecules from the region of low solute concentration to the region of high solute concentration.
References
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Saturday, July 4, 2020



