Simple Diffusion vs Facilitated Diffusion
What is Simple Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion
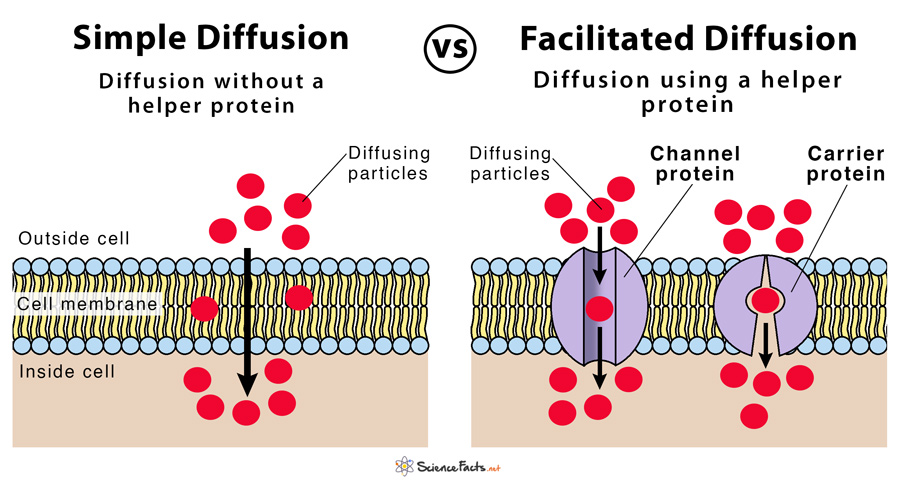
Both simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are passive transport processes that are vital to every cell in our body. Although they share some similar basic properties, their mode of operation differs in many aspects.
How does Simple Diffusion Differ from Facilitated Diffusion
| Basis For Comparison | Simple Diffusion | Facilitated Diffusion |
| The Process | Unassisted type of diffusion in which a particle moves from a region of their high concentration to a region of low concentration | Transport of substances across a biological membrane along the concentration gradient by means of a helper protein |
| Occurrence | Occurs directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane | Occurs through helper transmembrane integral proteins called carrier proteins or channel proteins |
| Helper Protein | Does not require a helper protein | Requires specific helper protein |
| Factors Affecting the Rate | The rate depends upon the membrane permeability, size, and the concentration gradient across the membrane | The rate depends upon temperature, diffusing distance, size, and concentration of the molecule |
| Substances Transported | Small molecules like water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethanol, and urea | Large biomolecules like glucose, amino acids, nucleic acids, and charged ions |
| Specificity | Non-specific to solute | Always solute specific |
| Nature of Substances | Permits the passage of only small and nonpolar molecules | Permits the passage of large polar molecules |
| Speed of the Process | Slow than facilitated diffusion | Fast than simple diffusion |
| Inhibition | No inhibitor molecule can inhibit the process | Can be inhibited by a specific inhibitor that binds to the helper protein molecule |
| Examples | 1. Diffusion of respiratory gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of the cell 2. Animals getting rid of their waste products like carbon dioxide, urea and uric acid | 1. Transport of biomolecules such as glucose, amino acids and nucleic acids inside the cell 2. Transport of ions such as sodium and potassium in and out of the cell |
What Characteristics do Simple Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion share
- In both the processes, the molecules move from a region of their high concentration to a region of low concentration, i.e., along the concentration gradient
- Both require energy expenditure by the cell and thus are passive transport mechanisms
- Presence of a membrane is necessary for both simple and facilitated diffusion
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Saturday, July 4, 2020



