Sepals
What is Sepal
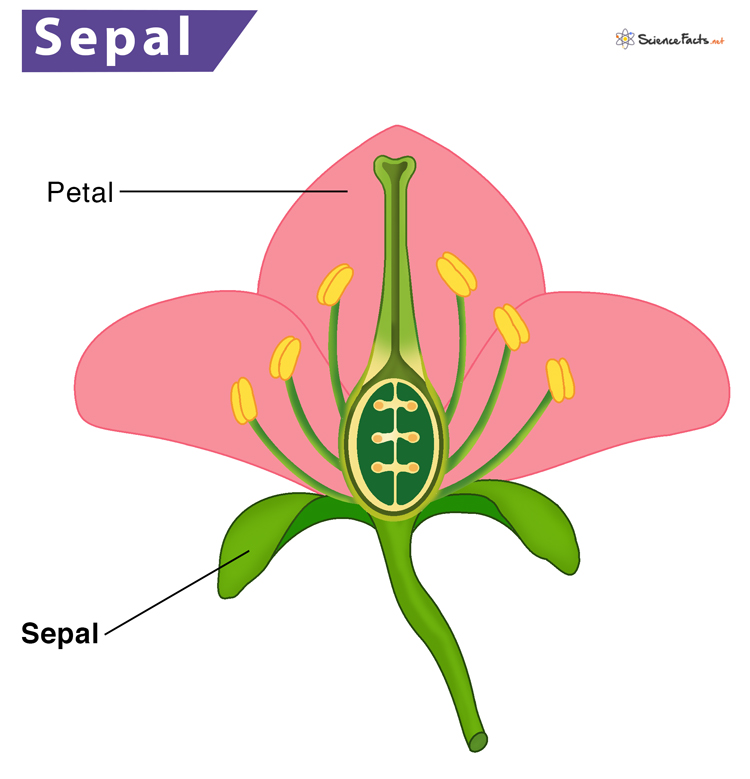
Sepals are small, leaf-shaped structures, forming the outer whorl of a flower. They are modified leaves, primarily green but can be of other colors too. Their number, size, and shape vary depending on the flower species. Sepals are either fused or separated. The sepals of a single flower are collectively called the calyx. They protect the flower bud and support the petals when in full bloom.
Structure
Sepals mainly consist of parenchyma cells, secretory cells called laticifers, tannin cells, and other specialized plants cell organelles. Green sepals comprise chloroplasts, whereas colored sepals contain chromoplasts within their cells. Along with plastids, they also contain differentiated palisade and spongy mesophylls.
Function
- Protect the reproductive organs within the flower.
- Enclose the floral bud until it is ready to bloom.
- Protect the bud and flowers from harsh environmental conditions.
- Protect flowers and fruits by emitting certain chemicals that ward off predators.
- In some species, sepals act like thorns to protect the flower.
- Support the petals when the flower is in full bloom.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, December 24, 2021