Root Hair
What is Root Hair
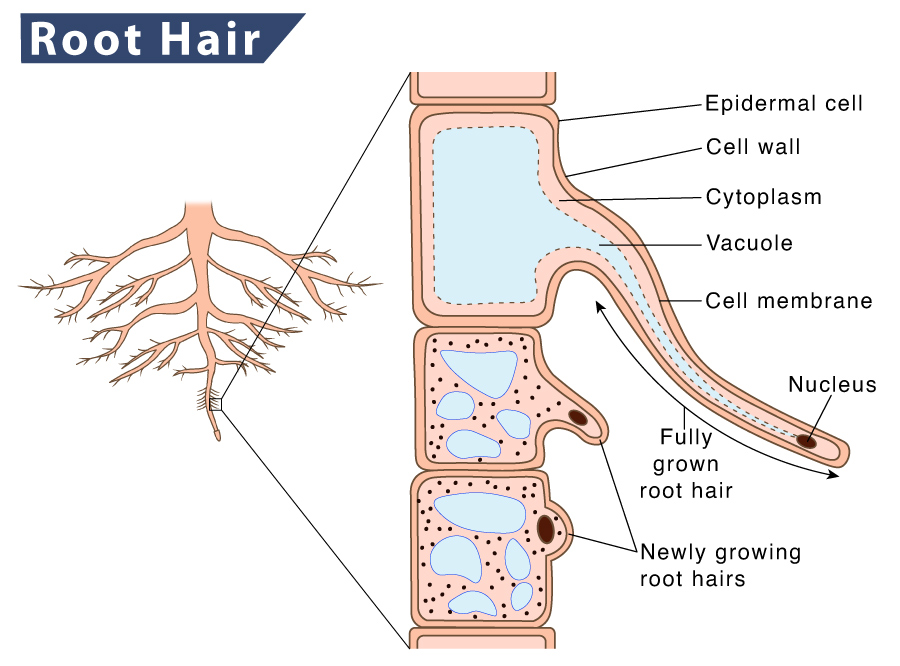
Root hairs are tiny, unicellular, hairlike outgrowth present on the outer surface of plant roots. They extend from the outer layer of a plant cell called the epidermis. Root hairs are continually being sloughed off by the soil and regrown.
The primary function of root hair is to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. A single root can have millions of root hair cells, increasing the overall surface area for water absorption.
Size
The dimension of root hair cells ranges between 15-17 μm in diameter and 80-1500 μm in length.
Structure
The epidermal cells present in the region of maturation of the root are responsible for the growth of root hair. A single root epidermal cell is roughly rectangular with a cytoplasmic extension on its lateral end. These long, tubular outgrowths are called root hair.
Like any other plant cell, it is bound by a cell wall and a semi-permeable cell membrane. It also possesses a large central vacuole and mitochondria lying on the cytoplasm. The mitochondria supply the required energy during the active transport of minerals and ions, i.e., taking up ions against the concentration gradient. Being a living cell, it contains a nucleus, which gets pushed to the corner by the vacuole.
Function: what do root hair cells do
Main function
The primary function of root hair is water and nutrient acquisition. These minute structures provide a large surface area for the active uptake of water and minerals.
Other functions
Some other roles of root hair include:
- Anchor the plant to the ground.
- Interact with soil microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi.
- Directly involved in the formation of root nodules in legume plants.
- Secrete some acids, such as malic and citric acid, which solubilize minerals by changing their oxidation state, making the ions easier to absorb.
FAQ
A: Root hair cells do not contain chloroplast.
A: Proton pumps present in the plasma membrane of root hair set up an electrochemical gradient that helps the root to absorb ions.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Wednesday, February 1, 2023