Reverse Osmosis
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)
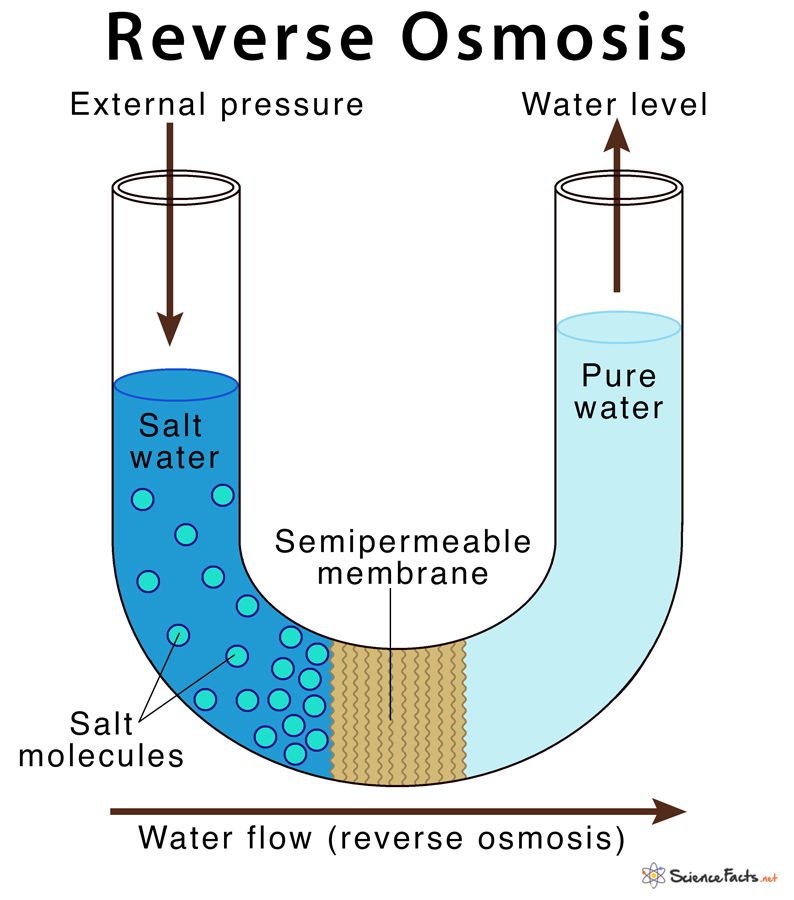
It is a technique of purifying water by removing dissolved impurities such as ions and minerals from the solution. In reverse osmosis, water is passed through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high solute concentration to a region of low solute concentration through the application of external pressure, thus in a direction opposite to that found in normal osmosis.
Principle of Reverse Osmosis
It works opposite to the principle of osmosis, the natural tendency of water with dissolved solutes to flow through a membrane from low to high solute concentration.
In the RO system, external pressure is applied to overcome the normal osmotic pressure of the solution that allows separation of pure water from their impurities. The impurities are removed based on the size and charge of the particle.
How does Reverse Osmosis Work
When a semipermeable membrane is placed between the pure water and salt water solution, on the application of external pressure from the salt water side, the water molecules are forced to cross the membrane towards the pure water leaving behind all its salts.
Thus in RO, the solvent moves from the region of low to high solute concentration in the solution.
Applications of Reverse Osmosis
- Purification of salt water and rainwater
- Helping in wastewater treatment plants
- Concentrating fruit juices and syrups without damaging the functions of proteins and enzymes
- Producing whey protein powders for the concentration of milk
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis
Advantages
- All dissolved and suspended impurities such as salt particles, colloids as well as bacteria and pyrogens are eliminated from drinking water
- Salts and excess minerals are removed from seawater (desalination) to make it fit for use in agriculture and drinking purposes
- Keeps the environment clean because of its eco-friendly nature
Disadvantages
- Smaller charged impurities such as sodium and calcium ions cannot be filtered through the RO membrane
- Dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen are not filtered out by RO membrane
- Some essential ions and minerals are unnecessarily removed from drinking water
FAQs
Ans. Unlike in reverse osmosis which is a non-spontaneous process requiring energy, osmosis is a spontaneous process involving the movement of solvent molecules from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration through a semipermeable membrane occurring without any energy expenditure.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023