Parts of a Stem With Their Structures and Functions
The stem is the central axis of the plant, which is mostly found above the ground, the root being the other part. They may be unbranched like those in a palm tree or branched like that of rose plants.
The stem is the connecting medium between the roots, the leaves, and the flowers, whose primary function is to provide mechanical support to the plant. The main woody stem of a plant is called the ‘trunk’.
What Are the Different Parts of a Stem
A typical plant stem consists of eight distinct parts, containing six elements and two organs. The six elements are: 1) nodes, 2) internodes, 3) terminal or apical bud, 4) lateral or axillary bud, 5) petiole and 6) pedicel. While the two organs are: 7) leaves and 8) flowers.
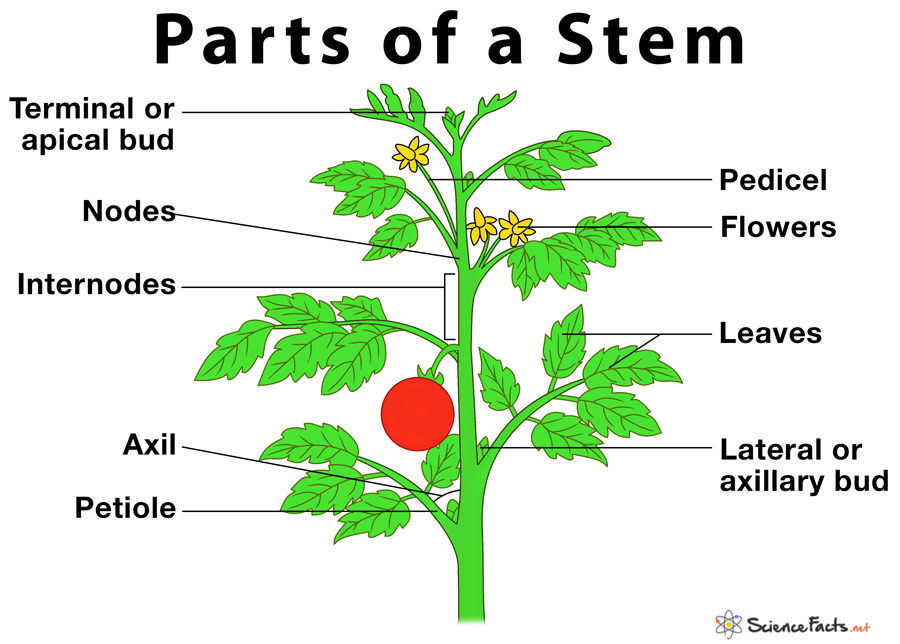
1) Nodes
They are the region of active division where the buds, leaves, aerial roots, and the branches originate. Nodes can hold several leaves and buds together in a stem.
Functions
- Helping the plant to form buds, leaves, and branching twigs
- Helping plants to heal from injury
- Providing additional structural support to the plant
- Reproducing new plant parts or even a complete plant by the process of stem cutting, like rose, salvia, dahlia, boxwood, etc.
2) Internodes
Also known as the ‘internodal’ zone, they are the regions between two successive nodes. Internodes are widely spaced between the nodes in most plants, while in few others, they are short, making the two adjacent nodes to be closely separated as found in dwarf conifers.
Functions
- Acting like blood vessels that carry and distributes food, water, and minerals from one node to another
- Providing height to the plant, greater the inter-nodal space more the height of the plant
3) Terminal or Apical Bud
It is the small extension found at the tip of the plant. Terminal buds are always in a state of division, thus contributing directly to the growth of the plant.
Functions
- Acting as the primary growing point in the stem
- Producing growth hormones that inhibit the growth of other buds in the stem (apical dominance), thus helping the plant to grow vertically upwards
4) Lateral Bud or Axillary Bud
It is the small bud that develops from the region between the stem and a leaf called axil. Lateral buds later give rise to a new stem. Although they mostly remain inactive, under favorable conditions of growth they develop into shoot, leaf or a flower, based on the requirement of a plant.
Functions
- Helping the plant to develop its lateral branches and leaves, the vegetative parts of a plant
- Helping the plant to develop flowers, the reproductive part of a plant
5) Petiole
The thin stalk of the leaf that connects the leaf to the node of the stem is called a petiole. A leaf with a petiole is called a petiolate leaf, whereas leaves without them are called sessile.
Functions
- Attaching the leaf to the stem and thus providing strength and support to the leaf
- Transporting water and minerals from the stem to enter the leaf and photosynthetic products to be distributed from the leaf to the rest of the plant
6) Pedicel
The short, slender stalk that attaches an individual flower in a cluster of flowers (inflorescence) is called a pedicel. A flower without a pedicel is called a sessile.
Functions
- Exposing flowers to the sun and wind so that they can attract pollinators like bees and insects for the purpose of sexual reproduction in plants
7) Leaves
They are the thin, flat organ of a plant that is generally green in color. Leaves are the main lateral appendage of the stem that arises from the nodes.
Functions
- Helping plants to produce food with the help of sunlight, carbon dioxide and water by a process called photosynthesis
- Helping the plant to cool down by losing water in the form of water vapor by a process known as transpiration
- Helping in exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in plants
- Helping in the reproduction of a specific group of sprout plants known as Bryophyllum
8) Flowers
They are the most colorful and attractive organ of a plant which varies widely in shape and size with every plant species.
Functions
- Helping in the sexual reproduction of plants
- Attracting pollinators like bees and other animals that help to transfer pollen grains from the male to the female reproductive part of the flower, a process known as pollination
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023




Nice account
I was wondering to such good notes to have ☺️