Parts of a Flower With Their Structure and Functions
Flowers are the reproductive part of a flowering plant. They are the most colorful and attractive organ of a plant body.
What are the Different Parts of a Flower
A typical diagram of a flower is divided into four main parts: 1) sepals, 2) petals, 3) stamen and, 4) carpel, each of them performing distinct functions.
When a flower has all the four floral parts, it is called a complete flower. A flower missing any one of them is called an incomplete flower.
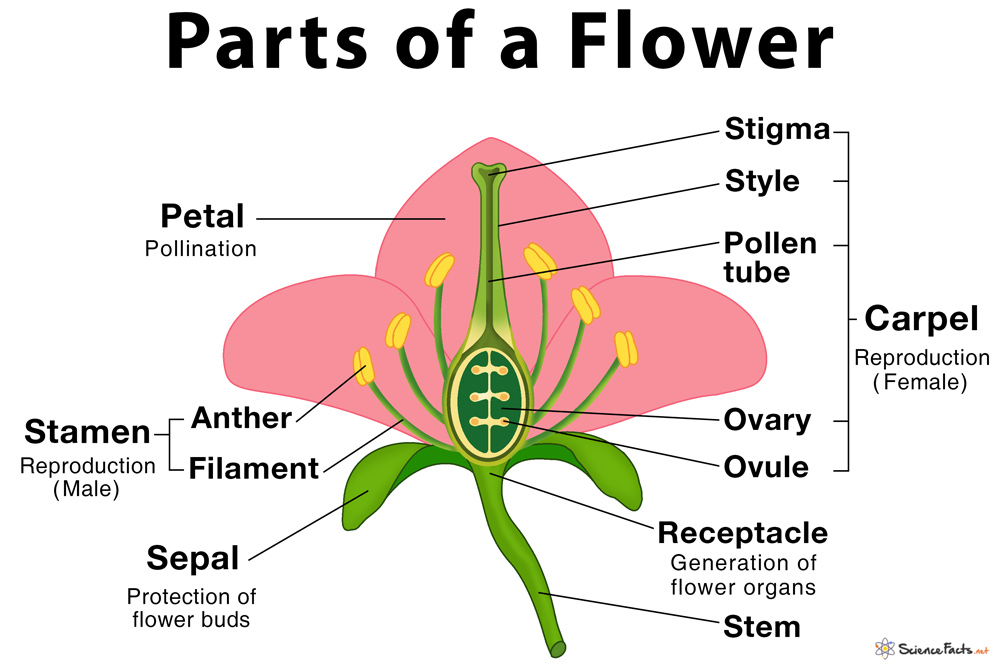
1. Sepals
They are modified leaves that enclose the developing flower. Sepals are the first essential part that grows in a flower, arising from the top of the stem.
Functions
- Providing protection to the young flower buds from an injury by forming a tightly closed area
- Giving structural support to a flower
2. Petals
They are modified leaf-like parts that surround the reproductive organs of a flower. Petals are the brightest and colorful parts of a flower that distinguish them from other parts.
Functions
- Protecting the reproductive structures in flowers
- Attracting pollinators like insects (e.g., bees, wasps, and butterflies), birds and other small mammals to transfer pollen from male to female reproductive part of a flower
3. Stamen
It is the male reproductive part of a flower. It consists of two main parts:
a) Anther – Yellowish sac-like structure present at the head of the stamen.
b) Filament – Slender stalk-like structure present at the tail of the stamen.
Functions
- Anther helps in producing and storing pollen grains
- Filament holds the anther and attaches it to the flower
4. Carpel
Female reproductive part of a flower that forms pistil. A pistil may contain a single carpel or multiple carpels fused together. It contains three parts:
a) Stigma – Head of the pistil that catches pollen grains.
b) Style – The stalk of the pistil. When pollen grains reach stigma, a tube-like structure grows through the style called pollen tube, which reaches the ovary.
c) Ovary – The base of the pistil that holds the eggs or ovules. The ovary later becomes the seed when the male and female reproductive cells fuse together, thereby forming the embryo, a process called fertilization.
Functions
- Stigma helps in receiving pollen grains and also in their germination
- Style supports the stigma and connects it to the ovary
- Ovary helps in developing, distributing, and nourishing the embryo
FAQs
Q.1. What are androecium and gynoecium?
Ans. The androecium is the male reproductive part of a flowering plant, which is composed of one or more stamens.
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of a flowering plant, which is composed of one or more carpels.
Q.2. What is a unisexual flower?
Ans. When a flower has either stamens or carpels, but not both of them, it is called a unisexual flower. Example: papaya and watermelon.
Q.3. What is a bisexual flower?
Ans. When a flower has both stamens and carpels, it is called a bisexual flower. Example: rose and mustard flower.
Q.4. Which part of a flower contains the ovary?
Ans. The ovary is the enlarged basal portion of the pistil where ovules are formed.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, July 3, 2020




it was great.
Everything is great keep up the good work
i like it
Thank you. Thi one is a great help for me.
I did not know flowers have male and female parts for reproduction.
I like so much to learn about the parts of a flower, it helps me a lot to know more about nature, flowers are very good.
It’s good
It’s nice site and it works perfectly
Very fantastic