Mitosis vs Meiosis
The primary goal of all living organisms on earth is to reproduce in order to survive and evolve, generation after generation. In multi-celled organisms (eukaryotes), the cells grow and reproduce using two different cell division processes — mitosis and meiosis.
What are Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis is the process by which somatic cells duplicate and divide their genetic material, forming two identical daughter cells. Meiosis, on the other hand, allows reproductive cells to divide twice to produce four non-identical daughter cells, each having half the genetic material of the parent cell. The former is used in eukaryotes mainly for cell growth and repair, while the latter is necessary for reproduction.
Compare and Contrast between Mitosis and Meiosis
Although both are similar in some ways, there are also many differences in their basic processes, steps, and the outcome. The important ones are listed below.
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
| Basis | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
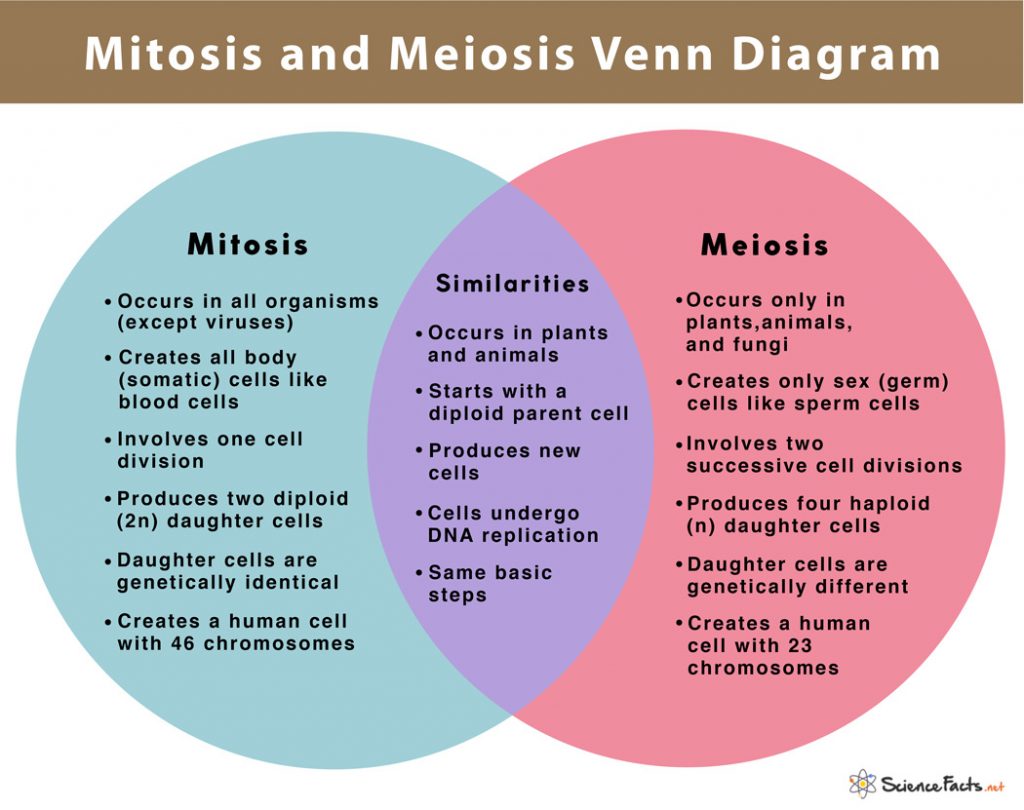
| 1. End Result | Produces two daughter cells. | Produces four daughter cells |
| 2. Chromosome Number | The daughter cells are diploid (2n). | The daughter cells are haploid (n). |
| 3. Genetic Composition | Daughter cells are genetically identical. | Daughter cells are genetically different. |
| 4. Main Purpose | a) Growth, repair, and replacement of old, damaged cells in higher organisms; a form of asexual reproduction in lower organisms (prokaryotes). b) Not involved in maintaining the chromosome number in organisms. c) Helps in cell multiplication during the early period of growth. | a) Formation of sex cells or gametes, necessary for reproduction in higher organisms. b) Maintains the chromosome number in the organism. c) Helps to maintain genetic diversity in the population. |
| 5. Takes place in | All organisms except viruses. | Only in animals, plants, and fungi. |
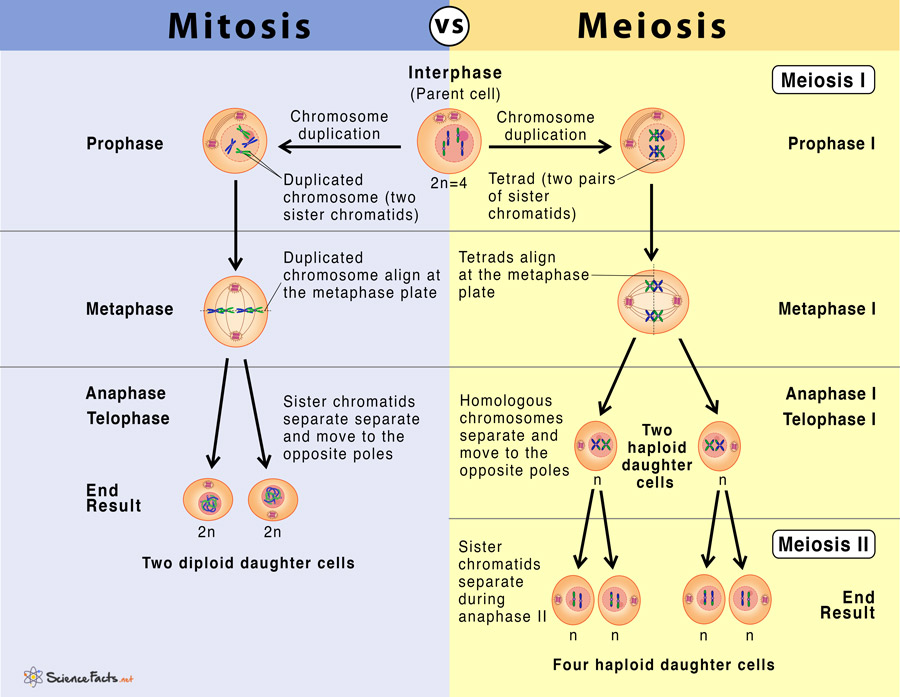
| 6. Number of Cell divisions | Involves one cell division. Steps: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. | Involves two cell divisions. Steps: (Meiosis 1) – Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I; (Meiosis 2) Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II. |
| 7. Cells it Produces | Creates all body (somatic) cells such as blood, liver, and skin cells except the germ cells. | Creates sex (germ) cells — eggs and sperms. |
| 8. Length of Prophase | Prophase is shorter than prophase I in meiosis. | Prophase I is longer than the prophase of mitosis. |
| 9. Formation of Synapsis and Crossing Over | Both are absent. | Both take place during prophase I. |
| 10. Formation of Tetrad | Absent | Occurs during prophase I. |
| 11. Number of Chromatids and Centromere | Each chromosome contains two chromatids and a single centromere. | Each chromosome contains four chromatids and two centromeres. |
| 12. Chromosome Alignment | Sister chromatids align along the center of the cell during metaphase. | Sister chromatids align along the center of the cell during metaphase I. |
| 13. Chromosome Separation | Sister chromatids separate during anaphase. | Sister chromatids do not separate during anaphase I. |
| 14. Cytokinesis | Occurs once at the end of telophase. | Occurs twice at the end of telophase I and telophase II. |
How are Mitosis and Meiosis Similar
- Start with a diploid parent cell.
- Are preceded by an initial growth period called interphase of the cell cycle, during which the DNA is duplicated. Thus the number of chromosomal duplication is the same in both the processes.
- Go through the same basic phases; prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Involve lining the duplicated chromosome (sister chromatids) along the center of the cell during the metaphase.
- Involve separation of sister chromatids forming daughter chromosomes during anaphase of mitosis and meiosis II
- End with the division of cytoplasm called the cytokinesis that produces new cells.
Conclusion
Considering the differences and the similarities, the basic significance of mitosis and meiosis is that they both involve cells to divide and form new cells. This makes them vital for the survival of organisms that reproduce sexually.
FAQs
Ans. Walther Flemming discovered the process of mitosis in 1879, while meiosis was discovered by Oscar Hertwig in 1876.
Ans. Cell division in prokaryotes does not occur through mitosis but undergoes a similar process known as binary fission.
Ans. Mitosis is the more common of the two processes in all living cells since it helps grow, repair, and replace the old and damaged cells. In contrast, meiosis occurs only in reproductive cells during the formation of gametes.
Ans. At the G2 checkpoint in both, it is evaluated whether any DNA is damaged in the cell to decide whether the cell should progress further in the cell cycle.
Ans. Some species employ both mitosis and meiosis because the former helps in the initial growth of the organism while the later is needed in carrying out their reproduction.
Ans. DNA is replicated during the S phase of interphase before the start of both mitosis and meiosis.
Ans. Although both are essential in higher organisms, meiosis has an advantage over mitosis in that the former helps create genetic variation within the population such that every individual is different from the other.
Ans. Spindle fibers help divide the DNA of the parent cell equally among the two resulting daughter cells both during mitosis and meiosis.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023




Thank you for the excellently presented information in this article, Mitosis vs Meiosis, it provided so many educational facts about them both.