Double Fertilization
Double fertilization is a fertilization mechanism in flowering plants or angiosperms. The process involves the fusion of one female gamete or egg cell (megagametophyte, or the embryo sac) with two male gametes (sperm cells).
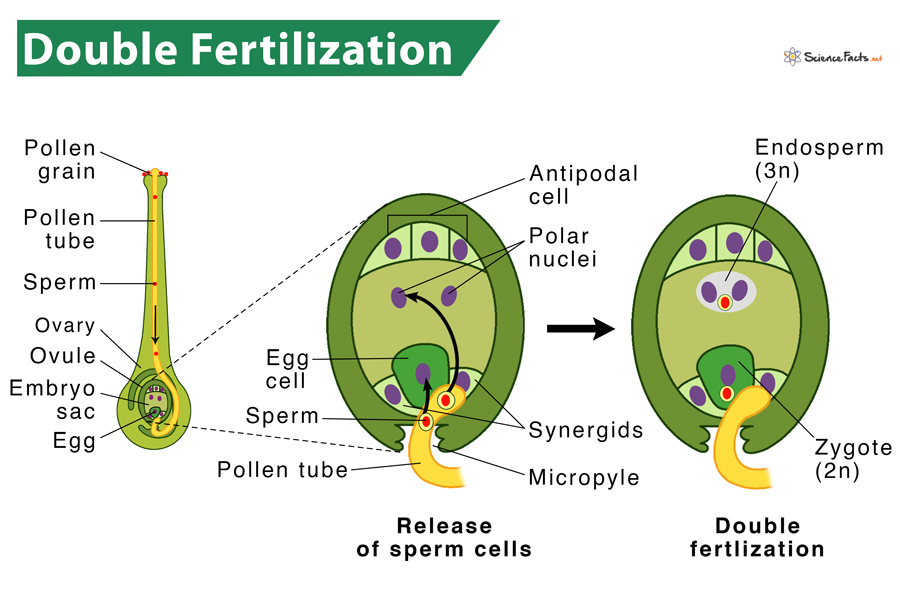
Out of the two sperm cells, one fertilizes the egg cell to produce a zygote, and the remaining one fuses with two polar nuclei producing endosperm. It is thus a part of the sexual reproductive process in such plants. Since two fertilization events coincide, it is called double fertilization.
The Process of Double Fertilization in Angiosperms
Double fertilization happens when pollen is deposited from the anther (male) to the flower’s stigma (female). Mature pollen grains or microspores contain generative and pollen tube cells.
Steps
- On reaching the stigma, the tube cell forms a pollen tube through the style until it reaches the ovule. Pollen tube development requires water, oxygen, and specific chemical indications. The style’s tissues support the pollen tube’s growth as it travels through the style to enter the embryo sac.
- The generative cell then migrates through the pollen tube to enter the ovary for fertilization. During this period, the generative cell divides to form two male gametes or sperm cells.
- Then, the synergid cells in the embryo sac guide the pollen tube by secreting specific chemicals. Later, the pollen tube enters the ovule sac through the micropyle.
- Out of the two sperm cells, one fertilizes the egg cell and forms a diploid zygote (2n). At the same time, the other fuses with the two polar nuclei, forming a triploid cell that develops into the endosperm (3n).
What does Double Fertilization Produce
The two end products of double fertilization are:
- Diploid zygote
- Primary Endosperm Nucleus
On completion of double fertilization, the entry of any other sperm gets blocked. The fertilized ovule transforms into a seed, whereas the ovary tissues become the fruit, usually enveloping the seed.
Post the fertilization event, the process of embryonic development begins. The zygote splits to form the upper cell (terminal cell) and the lower cell (basal cell). The basal cell transforms into the suspensor, which eventually develops a connection with the maternal tissue, helping transport nutrients to the growing embryo. The terminal cell also divides, producing a globular-shaped pro-embryo that develops into an embryo forming the baby plant.
Importance of Double Fertilization
- Helps in Energy Conservation: Here, plants do not invest energy in seed nutritive tissue until fertilizing an egg. Also, the endosperm nucleus is active and divides rapidly, quickly forming the nutritive tissue. It saves energy compared to fertilization in non-flowering plants.
- Allows for Rapid Seed Development: As two male gametes are involved in this reproductive process, seed development occurs faster than other forms of reproduction. The endosperm nucleus divides rapidly, allowing the embryo to grow fast.
- Increases Genetic Diversity: A form of sexual reproduction involving a male and a female gamete union ensures better genetic diversity than asexually reproduced species. Also, the progeny formed are better adapted to the changing environment.
- Increases Plant Life span: Genetically diverse plants are better adapted to the environment surviving than those formed through asexual reproduction.
- Provides a Food Supply for the Seed: The secondary product of fertilization, the primary endosperm nucleus, develops into a nutritive tissue called endosperm, providing nutrition to the growing embryo. Also, some flowering plants use this food resource during unfavorable environmental conditions when the new baby plant sprouts.
- Restoring the diploid Chromosome Number: Like all fertilization events, double fertilization restores the original diploid condition of the zygote through the fusion of haploid sperm and egg cells.
FAQs
Ans. The differences between double fertilization and triple fusion are as follows:
1. In double fertilization, two sperm cells fuse with an embryo sac. On the other hand, triple fusion is a part of double fertilization, involving the fertilization of two polar nuclei in the embryo sac using a single sperm.
2. Double fertilization forms a diploid zygote and triploid endosperm, while triple fusion forms only the endosperm.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023