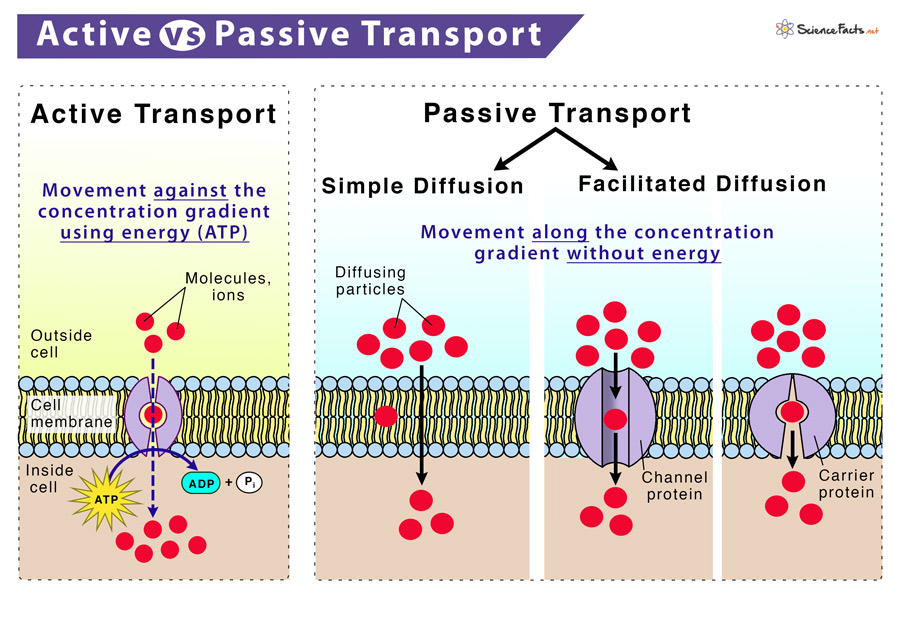
Active vs Passive Transport
Active and Passive transport are two important biological transport processes that help to move substances such as nutrients, oxygen, water, and other macromolecules within the cell, along with the elimination of waste products using different and contrasting mechanisms.
How is Active Transport Different from Passive Transport
| Basis For Comparison | Active Transport | Passive Transport |
| What Happens in the Process | Movement of substances across a biological membrane from a region of their low concentration to a region of high concentration | Movement of substances from a region of their high concentration to a region of low concentration |
| Nature of the Process | Highly selective process | Partly selective process |
| Rate of the Process | It is a fast process | It is a slow process |
| Direction of Transport | Unidirectional, against the concentration gradient of the substance | Bidirectional, along the concentration gradient of the substance |
| Influence of Temperature | Influenced by temperature | Not influenced by temperature |
| Involvement of Carrier Proteins | Requires carrier protein | Do not require carrier protein |
| Requirement of Energy | Requires cellular energy | Do not require cellular energy |
| Substances Transported | All ions, cells, and large molecules such as proteins, lipids, and complex sugars | Soluble molecules such as oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, lipids, sex hormones, and monosaccharides |
| Effect of Oxygen | Slows down when the oxygen content is reduced | Not affected by the level of oxygen content |
| Influence of Metabolic Inhibitors | Can be stopped by metabolic inhibitors | Not influenced by metabolic inhibitors |
| Types | Sodium-potassium pump, exocytosis, and endocytosis | Osmosis, diffusion, and filtration |
| Importance in Cell | To transport substances against their concentration gradient | To maintain the equilibrium, within and outside the cell |
Similarities between Active and Passive Transport
- Both processes help in the movement of essential substances inside the cell and also in the elimination of waste products
- Presence of a concentration gradient of the substance across the cell membrane is necessary for both the processes
- Both processes ensure that stability is maintained within the cell to keep it functional
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023