Heliotropism
Heliotropism is a tropic movement where plant parts track the sun’s direction. The leaves and flowers of certain plants orient themselves to face the sun as it moves across the sky from dawn to dusk. So, this kind of tropic movement is sometimes referred to as solar tracking.
The process enhances photosynthesis, increases plant growth, and attracts more pollinators. Thus, helping in the overall development of the plant.
Examples of heliotropic plants include sunflower, beans, alfalfa, arctic poppies, and buttercups.
In 1832, the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle first introduced the term heliotropism, derived from the Greek ‘helios’, meaning sun.
Its Types
Based on whether the plant part moves towards or away from the sun, heliotropism can be classified into two types:
- Positive heliotropism – Movement towards the sun’s direction.
- Negative heliotropism – Movement away from the sun’s direction.
How It Works
In Leaves
According to the sun’s position, some plant orient their leaves either perpendicularly (diaheliotropism) or parallelly (paraheliotropism).
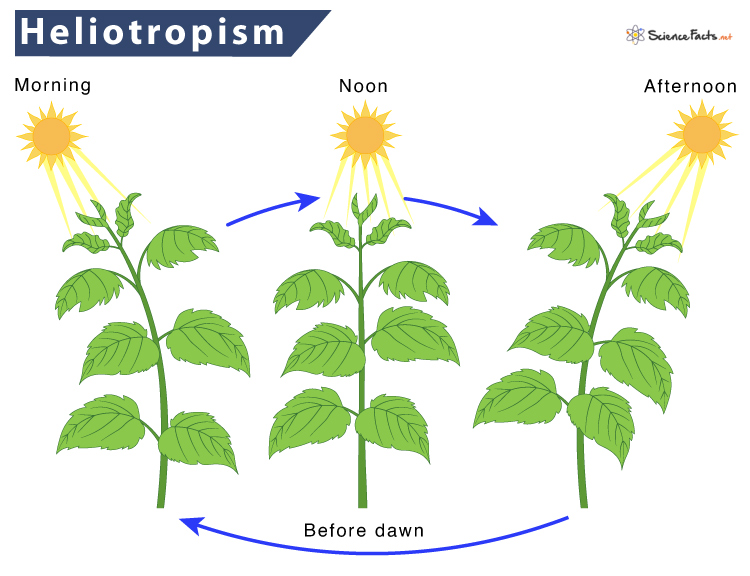
As the sun rises over the horizon, the leaves turn towards the sun in the east. Following the sun’s path, the leaves also turn from east to west as the day progresses. The next day, before dawn, the leaves reorient and face east to restart the solar tracking cycle. This phenomenon only happens on clear sunny days.
This rapid readjustment of leaves throughout the day is controlled by a specialized organ called the pulvinus. It is a fluid-controlled joint found in the petiole, the base of a leaf.
Advantage
The leaves orient horizontally in the morning and afternoon to capture the maximum sunlight. On the contrary, when the sun is most intense in midday, the leaves orient parallelly to avoid overheating and dehydration.
In Flowers
Some flowers slowly track the sun’s path across the sky from dawn to dusk. The sunflower is considered the most common example of a heliotropic flower. However, it only tracks the sun in its early developmental stage or the bud stage.
Many tropical flowers exhibit a modified form of heliotropism where they move opposite to the sun’s direction to reduce the chance of overheating (negative heliotropism).
Advantage
As the flowers face the sun, their temperature rises. This added warmth attracts more pollinators, enhancing fertilization and seed development.
Heliotropism vs. Phototropism
In heliotropism, the plant movement is guided by the sun. While in phototropism, the directional movement occurs in the presence of any light source.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, June 3, 2022