Electromotive Force (EMF)
What is Electromotive Force (EMF)
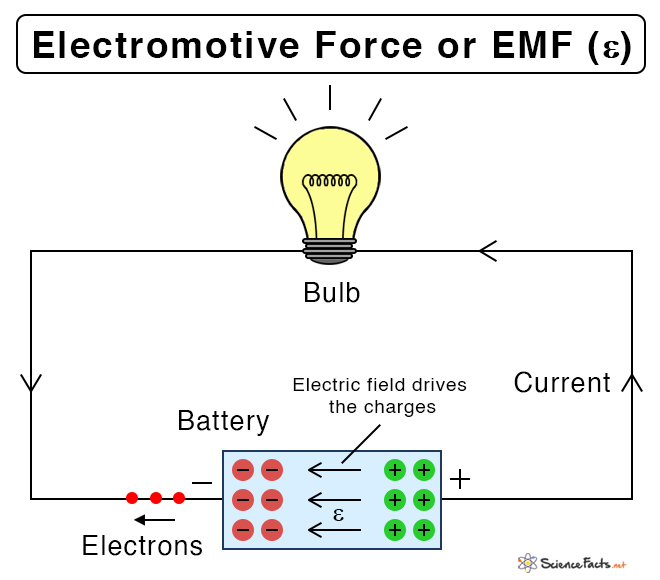
Electromotive force, or emf, is the energy required to move a unit electric charge by an energy source such as a battery, cell, or generator. It is defined as the potential difference across the terminals where there is no current passing through it, i.e., an open circuit with one end positive and the other end negative.
In reality, the electromotive force is not a force but a measure of energy. The source converts one form of energy into electrical energy. For example, a battery converts chemical energy, and a generator converts mechanical energy.
The term electromotive force was coined by Italian physicist and chemist Alessandro Volta, who invented the electric battery in 1800.
Electromotive Force (EMF) Equation
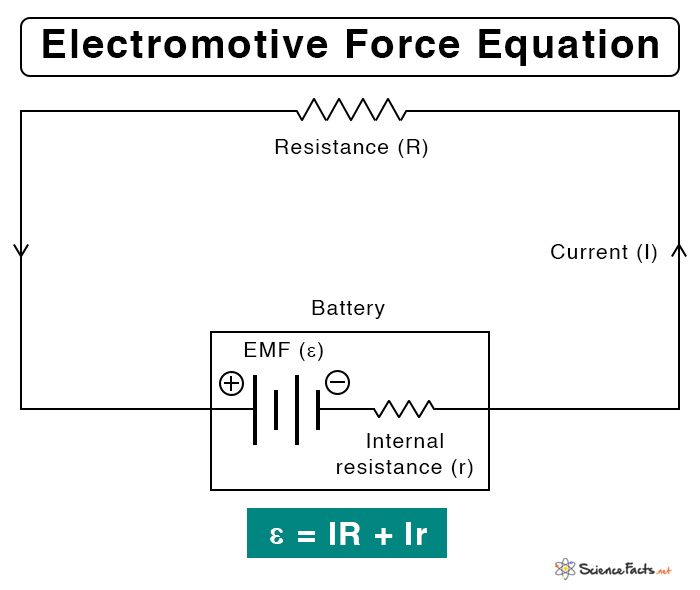
Suppose a circuit consists of a battery and a resistor. The electromotive force can be calculated using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law. The following formula gives its value.
ε = IR + Ir
Where,
I: Current passing through the circuit
R: Resistance of the resistor
r: Internal resistance of the battery
Symbol: ε, Greek letter epsilon
Using Ohm’s law,
V = IR
Therefore,
ε = V + Ir
A voltmeter is used to measure the EMF.
SI Unit
The electromotive force is measured in Volt, which is its SI unit. A Volt is defined as Joule per Coulomb.
Volt = Joule/Coulomb
Dimension
The dimension of electromotive force is [M L2 T-3 I-1]
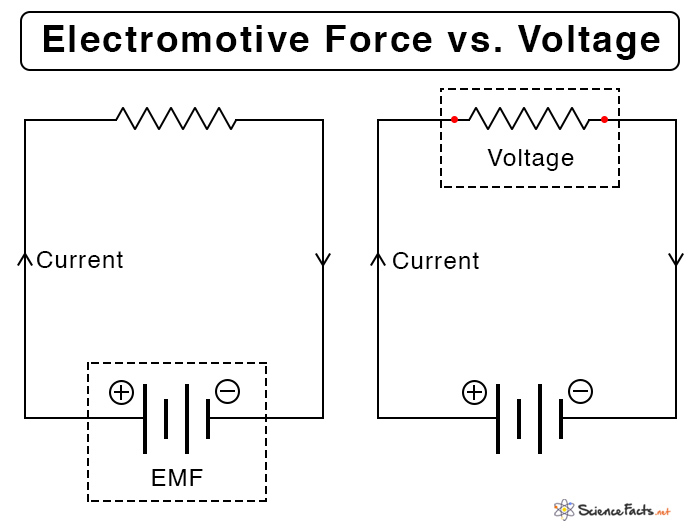
Electromotive Force (EMF) vs. Voltage
As mentioned earlier, the electromotive force is the terminal potential difference when no current flows through it. The following table lists the differences between the emf and the potential difference or voltage.
| Electromotive Force (EMF) | Potential Difference or Voltage | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Amount of energy supplied by the source to a unit charge | Energy used by unit charge to move from one point to another in a circuit |
| Symbol | ε | V |
| Formula | ε = V + IR | V = IR |
| Magnitude | Greater than voltage | Less than EMF |
| Where is it measured | Between the endpoints of the source when no current is passing through it | Across a resistor, when current is flowing through the circuit |
| Measuring device | EMF meter | Voltmeter |
| Source | Light (solar cells), chemical reactions (battery), and heat (thermocouple) | Cell, battery, and generator |
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023


It’s a good site
Nice
I like the article
Hey there, I love your blog! I can totally relate to your point as I work as a medical assistant for a BPO provider.